Amiibo
Amiibo are NFC figures made by Nintendo, used in games in different forms (different in each game). It can be used with the New3DS and the Old3DS with an IR peripheral.
Technical specifications
See also here.
Specifications can be found on this image, which is a compilation of screenshots made by scanning a Samus amiibo with the Android App "NFC TagInfo":
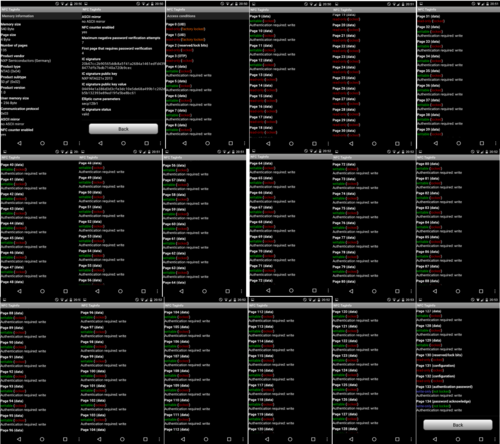
See here regarding the Amiibo encryption.
The NFC tag for Amiibo is NTAG215.
AUTH_PWD
The NFC 32bit password for the PWD_AUTH command(for enabling write-access to the encrypted NFC pages / etc), appears to be generated from unknown data that doesn't change when the Amiibo data pages are being updated.
NTAG215 commands
Amiibo reading
- GET_VERSION
- READ, startpage=0x03
- PWD_AUTH
- FAST_READ: startpage=0x00, endpage=0x3B
- FAST_READ: startpage=0x3C, endpage=0x77
- FAST_READ: startpage=0x78, endpage=0x86
Therefore, *all* pages from the Amiibo NFC tag are read, including the configuration pages at the end.
Amiibo writing
- Use the same commands under the above reading section, then use those first 3 commands again.
- Multiple WRITE commands for writing to pages 0x04..0x0C. The first byte for page[4] is zero here.
- Multiple WRITE commands for writing to pages 0x20..0x81.
- Use the last 3 commands from the above reading section.
- WRITE: page=0x04, same data as before except first byte is 0xA5 this time.
- FAST_READ: startpage=0x04, endpage=0x04
NFC pages
Each page is 4-bytes, there is a total of 0x87/135 pages. The following is the structure of the NFC pages:
| NFC page | Total pages | Raw byte offset in EEPROM | Total byte size | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 4 | 0x10 | 0x10 | Same as standard NTAG215: 9-byte serial-number, "internal" u8 value, two lock bytes then the "Capability Container (CC)" page. |
| 4 | 1 | 0x10 | 0x4 | Last 3-bytes here are used with the following HMAC. The first byte is normally 0xA5. The remaining bytes are initially(before the Amiibo is written to) all-zero. Byte[2] here is increased each time the Amiibo is written to. |
| 5 | 0x14 | The system crypts 0x1A0-bytes with a buffer containing data loaded from here. | ||
| 0x20/32 | 8 | 0x80 | 0x20 | SHA256-HMAC over 0x1DF-bytes: first 3-bytes are from the last 3-bytes of page[4], the rest is over the first 0x1DC-bytes of the plaintext data. |
Encrypted data buffer structure
| Encrypted buffer offset | Byte offset in the actual NFC data, relative to page[5] | Raw byte offset in NFC EEPROM | NFC page | Byte size | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0x0 | 0x0 | 0x14 | 0x5 | 0x20 | |
| 0x20 | 0x8C | 0xA0 | 0x28 | 0x114 | |
| 0x134 | 0x1A0 | 0x1B4 | 0x6D | 0x54 | |
| 0x188 | 0x20 | 0x34 | 0xD | 0x18 | This data is included in the crypto buffer, even though this data isn't actually encrypted(this is part of a hash). |
Structure of the plaintext data
| Offset | Size | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 0x0 | 0xB0 | Amiibo settings are stored within here. |
| 0xB0 | 0xD8 | AppData, for the user-application with the programID specified in the above Amiibo settings. The data stored here is application-specific. |
| 0x188 | 0x18 | Not used in "decrypted" form, since this isn't encrypted to begin with. |
Structure of Amiibo settings
| Offset | Size | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 0x0 | 0x1 | Unknown. The low 4-bits here are copied to the struct used with NFC:GetAmiiboSettings. |
| 0x1 | 0x1 | Unknown. The low 4-bits here are copied to the struct used with NFC:GetAmiiboSettings. |
| 0x2 | 0x2 | ? |
| 0x4 | 0x2 | u16 big-endian, unknown. |
| 0x6 | 0x6 | ? |
| 0xC | 0x14(10*2) | UTF-16BE Amiibo nickname. |
| 0x20 | 0x60 | Owner Mii. |
| 0x80 | 0x8 | Application programID for the AppData, zero otherwise. |
| 0x88 | 0x4 | ? |
| 0x8C | 0x4 | ? |
| 0x90 | 0x20 | Probably a SHA256-HMAC hash. |